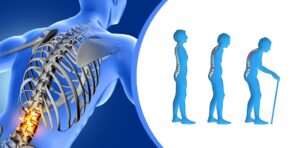
It is when bones become brittle as a result of the decrease in the density of bone tissue. Osteoporosis in the elderlyIt causes thinning of bones due to calcium loss. It can increase the risk of becoming more prone to falls and fractures. Therefore, it is an important health problem for elderly individuals and precautions should be taken to protect bone health.
Symptoms of Osteoporosis in the Elderly
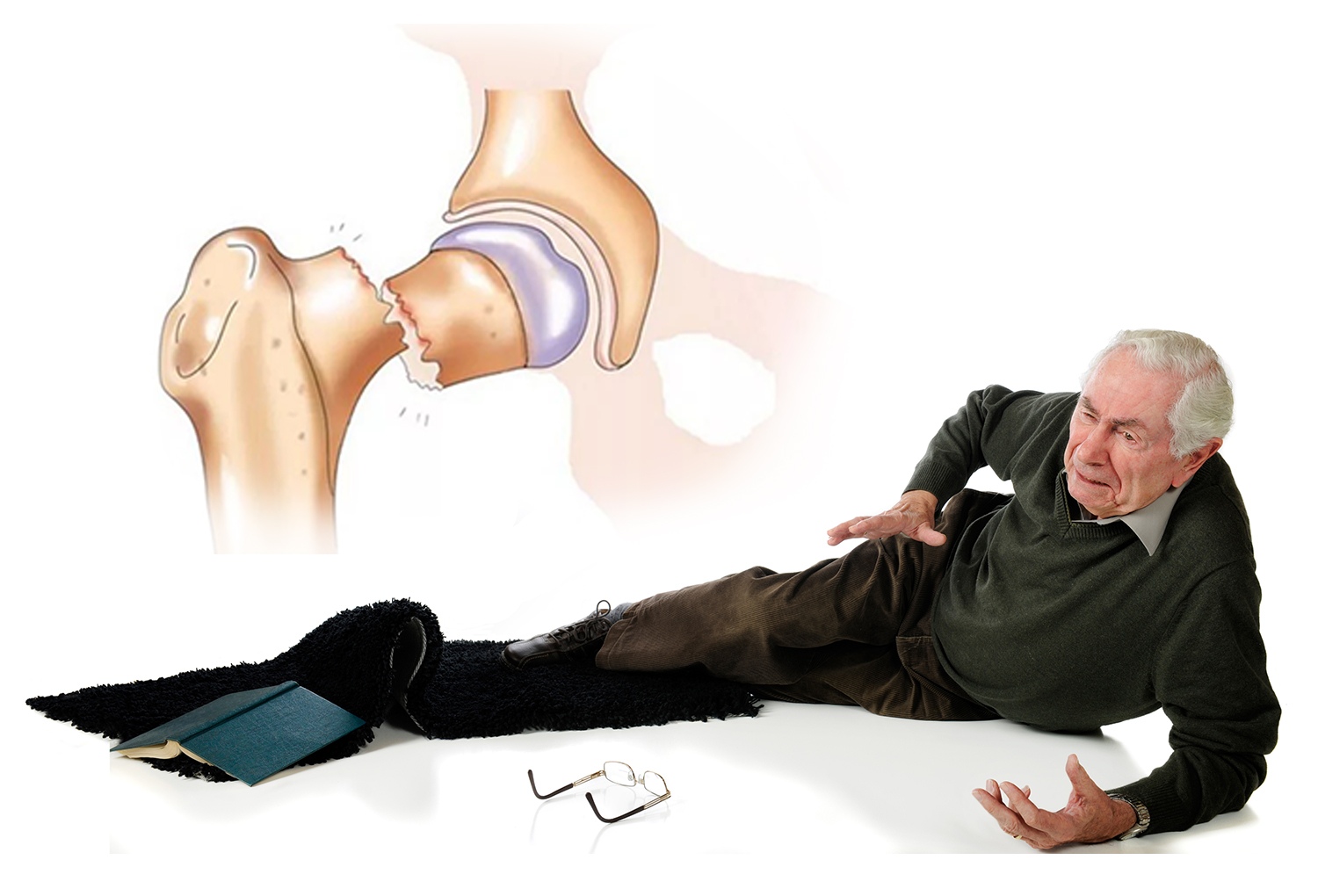
It can cause the bones of the spine to weaken, which can lead to a hunchback. As bones weaken, a person may lose height over time. Chronic pain such as back, waist and neck pain may occur. It can cause bones to break more easily. Hip, wrist and spine fractures are especially common. Low energy levels, fatigue, and fatigue may be common. Doctors can use bone density measurements to assess risk and make a diagnosis.
It may mean that the jaw bones may also be affected, leading to tooth loss. Symptoms of osteoporosis in the elderly It progresses silently before reaching very advanced levels. It is important for elderly individuals to have regular check-ups to maintain bone health and reduce risk factors. It is also important that they maintain a balanced diet and exercise regularly. If symptoms or risk factors are present, appropriate treatment and precautions should be taken under the guidance of the doctor.
Factors That Cause Osteoporosis in the Elderly
As we age, the density and quality of bones decrease. It increases the risk. Family history can influence the risk of the disease. If you have a family history of it, this may increase your risk. Estrogen levels decrease in women after menopause. This can reduce bone density and increase risk. Calcium is important for the formation and maintenance of healthy bones. Insufficient calcium intake may increase the risk.
Vitamin D supports the absorption of calcium. Vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of the disease. Some medications can cause bone loss. Particularly long-term use of corticosteroids may increase the risk. Regular physical activity is important for maintaining bone health. Not being physically active may increase the risk. Having a thin body structure may increase the risk.
Some health problems, especially conditions such as thyroid diseases and intestinal problems, may increase the risk. Osteoporosis in the elderly It is necessary to take vitamin D to reduce the risk. It is important to be active, not to smoke, and to adopt a healthy lifestyle. It is also important to take your medications regularly as recommended, especially if you have a related health problem. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to assess your risk and take appropriate precautions.
Treatment of Osteoporosis in the Elderly
Hormone replacement therapy may be used to treat osteoporosis, especially after menopause. However, risk and benefit must be carefully evaluated. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake may help support bone health. Your doctor should recommend supplements based on your needs. Regular exercise can help strengthen bones and increase their density.
Weight-bearing exercises and resistance training, in particular, are beneficial for bone health. A healthy diet supports bone health. Foods containing calcium and vitamin D, such as dairy products, green leafy vegetables, and salmon, are important. It is important to avoid harmful habits.
Bone fractures in elderly individuals usually occur as a result of falls. Therefore, it is important to take safety precautions at home and reduce the risk of falls. Its treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Treatment options should be determined based on the patient's health history and condition. Osteoporosis in the elderly It is important to cooperate with your doctor to manage and reduce the risk of fracture.